25 March 2023 7:00 AM
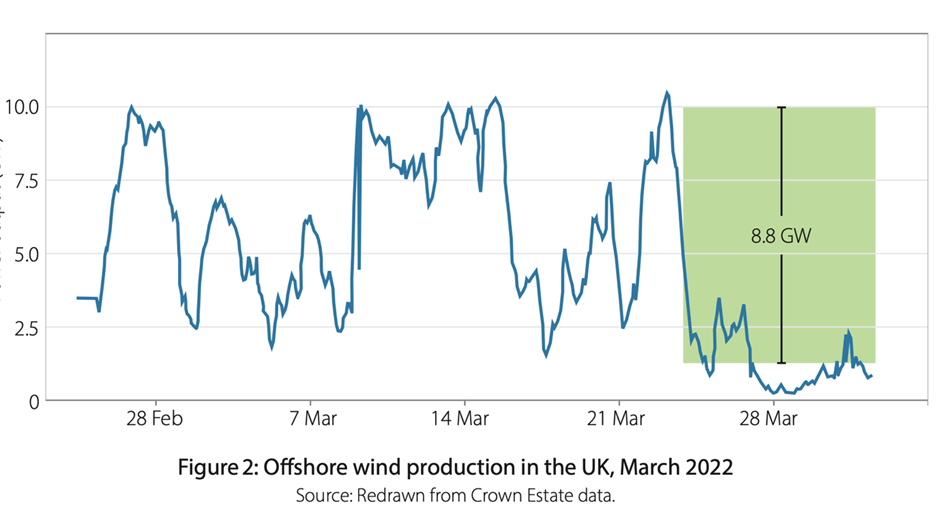
The installed nominal generating capacity in the EU and U.K. in 2021, shown by the brown dashed line, was 236 GW, but the highest daily output was only 103 GW on March 26th. The unreliability is shown to even greater effect in the second graph that plots the wind generated offshore in the U.K. in March last year.
For eight days at the end of the month, power generation slumped, presumably, says Allison, because the wind speed halved. The 8.8 GW daily loss over the period was noted to be 1,000 times the capacity of the world largest grid storage battery at Moss Landings in California. When it comes to the enormous batteries needed to store renewable power, Allison notes the problems with safety, as well as mineral shortages. Batteries will never make good the failure of offshore wind farms, even for a week, and he points out they can fail for much longer than that.
Others have recently looked in more detail at the costs of battery storage. The American lawyer and mathematician Francis Menton, who runs the Manhattan Contrarian site, reviewed recent official cost reports and found that “even on the most optimistic assumptions” the cost could be as high as a country’s GDP. On less optimistic assumptions, the capital cost alone could be 15 times annual GDP. Last year, Associate Professor Simon Michaux warned the Finnish Government that there were not enough minerals in the world to supply all the batteries needed for Net Zero. Michaux observed that the Net Zero project may not go fully “as planned”. Meanwhile, Menton concluded, with an opinion that some might consider unduly charitable: “It is hard to avoid the conclusion that the people planning the Net Zero transition have no idea what they are doing.”
Professor Allison has done his sums based on basic physics and freely available information. “Whichever way you look at it, wind power is inadequate. It is intermittent and unreliable; it is exposed and vulnerable; it is weak with a short life-span,” he concludes.
-
Tags
#United Kingdom